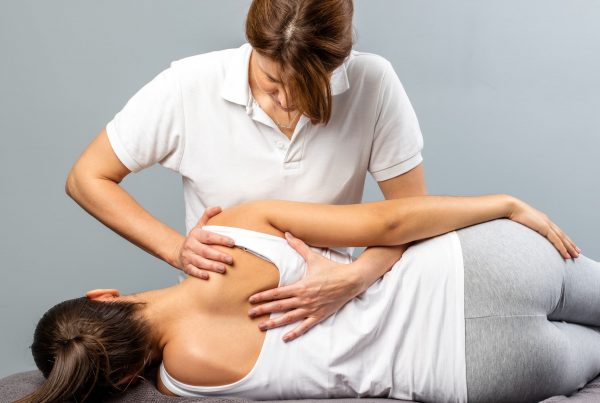
What is a Disc Injury?
A disc is like a cushion between vertebrae for shock absorption, force distribution and allows mobility.
The outer part (annulus fibrosus) is made of concentric layers of sheets of collagen at different angles and distributes pressure. The inner part (nucleus pulposus) is a jelly-like substance with proteins. This must be well hydrated as it relies on water to remain pliable and dehydrates with age and compression. It is vital to increase hydration levels to return the disc to its maximum height when injured.
DISC INJURY SYMPTOMPS AND TYPES
Symptoms
You may experience some or all of the following symptoms:
- low back and/or leg pain
- pain in glutes and hips,
- tingling, numbness of legs and feet,
- pain bending forward, backwards, rotation or combined movements.
Types of Disc Injuries
Annular strain/tear
All structures still intact but distorted, compressed and overstretched. It can be extremely painful.
Bulge/ Protrusion
Nucleus is very compressed and pushes the outer layers but hasn’t spilled out. It’s squashed and distorted in different areas but not pressing on nerves.
Herniated/Slipped
Inner nucleus has protruded through outer layers. Herniation with nerve compression. It’s still attached to the main body of the disc.
Sequestrated
Herniation has protruded through outer layers and detached. Random nerve compression, like a loose body. It can’t be controlled.
Cauda equina
It is a medical emergency. If you experience bilateral leg pain, severe weakness or numbness in both legs, not improving, saddle numbness around the genital and anal area, loss of bowel and bladder control, abnormal urination and defecation go to A & E.
DISC INJURY CAUSES
- Age. As your body ages ligaments have decreased blood supply, becoming harder and less elastic. Loss of joint height causes the segment to become more unstable. However, active children and young adults can suffer disc injuries too.
- Repetitive heavy lifting movements (exercises or work)
- Long distance and repetitive driving. The vibrations will damage the disc (lorry drivers are more susceptible to disc injuries)
- Overweight. It puts more pressure on the joints and squashes the discs in between.
DISC INJURY DIAGNOSES
Diagnosis is based on full medical history, physical examination to test muscles strength and reflexes. Images test, will allow the therapist or professional to determining the disc injury location.
The most common imagery test are:
- X-ray
- TC scans
- MRIs
DISC INJURY TREATMENTS
Medical
Your GP will prescribe a combination of:
- anti-inflammatories
- pain relief
- muscle relaxant drugs
- or steroid based injections
Please note these have many adverse gastrointestinal effects and can be addictive. They won’t solve any musculoskeletal underlying causes.
Natural
Hands on treatment
Manual therapy: You can try Physiotherapy, Osteopathy, Acupuncture. These are evidence based interventions proven to work.
A combination of manual therapy techniques will be selected by our experts after taking into account your past medical history, spinal mechanics, aggravating and maintaining factors, lifestyle.
When you are out of the acute phase you will be introduced to Pilates to strengthen core and glutes. You may need to make some lifestyle modifications addressing safe technique, correct sitting posture at desk, sleeping position. We have specialist therapists to advise you on this.
Home treatment
It is important for you to change bad posture habits, some tips are:
- Increase hydration, especially at night when the disc imbibes from the vertebral end plates. It plumps up becoming longer and thinner, decreasing compression.
- Rest
- Ice on painful area 5-10 min repeat every few hours.
- Ice gel, magnesium lotion (muscle relaxant).
We can help you!

DIAGNOSE

CONDITIONS

TREATMENTS
Treatments that can help
Here are some treatments that can help with Disc Injury Pain:
- Massage (Soft Tissue)
Help decompress the nerve impingement due to tight muscles - Osteopathy
Helps restore normal movement due to misalignment and decompress nerve impingement - Physiotherapy/Sports Therapy
Helps stabilise weak areas and restore normal movement - Acupunture
Helps to loosen up the tissue decompress the nerve impingement in tight muscles