Cellulite: what it is, causes and how to prevent it
What is cellulite?
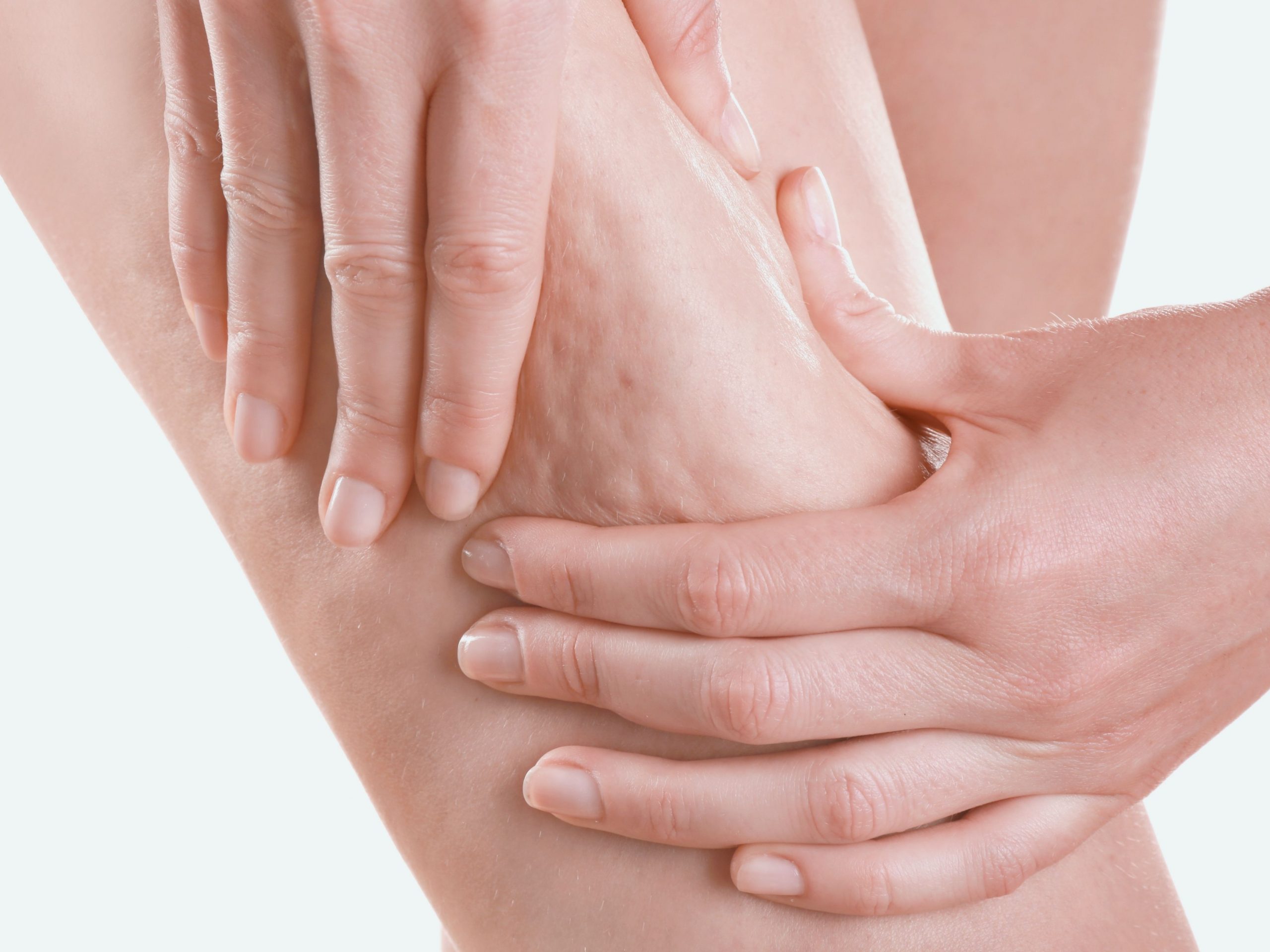
Cellulite is a metabolic condition characterized by physiological changes in the basic connective tissue, in the microcirculation and in the size of adipocytes (fat cells). Cellulite resides inside the adipose pad or subcutaneous cellular tissue. It is based on a microcirculation insufficiency that, according to its evolutionary stage, modifies the disposition of the basic connective tissue.
Cellulite generates an unwanted appearance (orange peel skin). You can notice it on thighs, buttocks, upper arms, abdomen and sometimes on the breast. Usually, It appears in periods of hormonal changes such as puberty or pregnancy.
Cellulite may affect women of all ages and sizes (teens, too). In fact, it affects the vast majority of women. About 90% of women will notice cellulite somewhere on their bodies at some point of their life. On the other hand, the percentage is much lower in men, approximately 10%. However, with little changes to your lifestyle it is possible to prevent cellulite or at least control it.
How is it formed?
There are 3 main facts that took place in the formation of cellulite. First, cellulite is formed when adipocytes increase in number or volume. Adipocytes are fat cells that, by increasing their size, can also cause compression of the capillaries. Second, there is an alteration in lipogenesis. In other words, the body accumulates more fat than it uses (lipolysis). Third, there is water retention, it produces swelling due to lack of drainage. As a result, you will notice that orange peel skin!
On the other hand, cellulite could be just part of a major problem such as poor circulation, inadequate diet, hormonal problems or even food intolerance. For this reason, it is important to make an early diagnosis. Even better, you can do some modifications to your lifestyle in order to prevent cellulite.
Symptoms
The most visible signs of cellulite are:
- Rough appearance (orange peel: holes and irregularities).
- Edema or bulges.
- Slight sensation of heaviness.
- You may notice nodules to the touch.
- Little mobility of the skin on the deepest planes.
- When pressing with the fingers the mark remains visible.
- Hypersensitivity to touch or in some cases to friction.
Causes
- Genetics: Family history of obesity and cellulite.
- Lack of exercise or sedentary lifestyle.
- Inadequate diet: excess calories and sodium and processed food.
- Stress.
- Consumption of alcohol.
- Smoking.
- Wearing inappropriate clothing such as tight clothing or very high heels.
- Spending long periods of time on your feet.
- Hormonal factors: High levels of estrogens leading to edema. These changes usually occur with processes such as puberty, pregnancy, menopause, premenstrual period or consumption of contraceptive pills. Therefore, they trigger or worsen cellulite if it already exists.
- Circulatory disorders that accumulate toxins making their elimination difficult.
Grades of cellulite (appearance of the skin)
First grade: the orange peel is not yet observed.
Second grade: orange peel appears when the skin is compressed.
Third grade: orange peel appears when standing up.
Fourth grade: orange peel is permanent.
Tips to prevent cellulite
There is no magic formula to eradicate cellulite, but it is possible to prevent it. The way to achieve it is to modify some habits, some of them are:
- Limit caffeine intake.
- Avoid states of stress. Nerves, anxiety and constant tension can worsen or trigger a cellulite process.
- Don´t smoke. It generates dysfunction in your circulation and prevents the absorption of vitamins.
- Have a healthy diet. Avoid the consumption of refined foods that generate a greater amount of waste products or toxic substances, as well as the accumulation of fats.
- Reduce or avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages because they generate toxic substances in the body, affecting the normal functioning of the liver and kidneys.
- Increase the consumption of fibers. It helps regulate intestinal transit.
- Increase water consumption. It helps to maintain a constant active circulation, oxygenating the blood and facilitating the disposal of toxic substances.
- Exercise. It stimulates circulation – both of the cardiovascular system and of the lymphatic system.
- Avoid tight clothing and high heels.
- Incorporate into your routine 1 or 2 weekly sessions of lymphatic drainage. It drains toxins out of your body and improves circulation.
We hope this information is useful for you. If you have any questions about our treatments, please contact us. You can find us in Mill Hill Broadway and Islington. If you like this blog, please share!
We are always happy to help.