4 Nutrition tips to Reduce Lymphoedema Risk after Orthopaedic-surgery
Orthopaedic surgery can place significant stress, damage or even remove part of your lymphatic system. Your immune system plays a vital role in maintaining fluid balance and immune defense. However, after orthopaedic or any type of surgery, especially procedures involving lymph node removal or disruption, the lymphatic network may become compromised, leading to fluid accumulation and persistent swelling known as lymphoedema. Among other strategies, proper nutrition is a crucial to reduce lymphoedema risk, yet often overlooked; it is also a key element of post-surgical care that supports lymphatic health, improves and speeds up healing, and reduces the risk of developing other secondary conditions. Let’s see how…
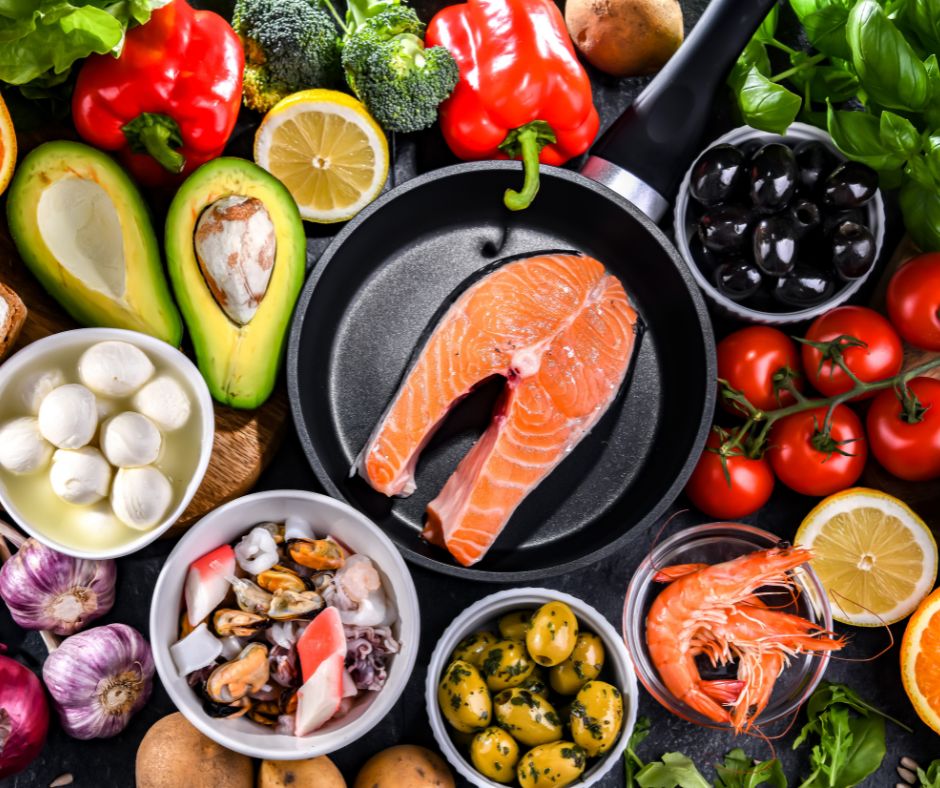
Inflammation is a natural response to surgery, it means you are in a recovery process, but excessive or prolonged inflammation can worsen lymphatic congestion, edema and turn into lymphoedema (also caused by damage in your lymphatic system). After surgery, your lymphatic system can be more vulnerable to fluid retention leading to lymphoedema. Eating properly to reduce systemic inflammation and oxidative stress is key to avoiding chronic inflammation. Polyphenols, natural antioxidants found in colorful fruits and vegetables, specifically target inflammation and support healthy lymphatic vessel function. Weight management through a balanced, calorie-controlled diet also improves lymphoedema symptoms and reduces limb swelling by lowering pressure on lymphatic ducts. Next a list of some foods you can introduce to your daily diet:
Post-orthopaedic surgery Nutrition:What to Eat to Reduce Lymphoedema Risk
1. Eat Foods to Promote Circulation and Reduce Inflammation
Focus on whole, unprocessed foods that contain anti-inflammatory nutrients, antioxidants, and healthy fats, for example:
Leafy greens
Detoxify the body, are full of antioxidants and provide magnesium for circulation and muscle relaxation, allowing lymphatic and vascular flow. Some that you can include are:
Common Leafy Greens
Spinach, kale, lettuce (romaine, butterhead, iceberg, leaf, etc.), Dandelion, Swiss chard, collard greens, mustard greens, arugula (rocket), cabbage (green, red, savoy, napa), etc.
Herbs often used as greens (have same properties)
Parsley, cilantro (coriander leaves), basil, dill, mint.
Berries
They contain antioxidants and flavonoids that reduce oxidative stress and inflammation that can block lymph flow. Some of them are: raspberry, blueberry, blackberry, cranberry, gooseberry, etc.
Citrus fruits
Such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are rich in vitamin C, which supports immune and lymph vessel function.
Healthy fats
Most known and easy to find in stores are: avocados, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish (such as salmon). All of them provide omega-3 fatty acids that decrease chronic inflammation and promote vascular health. Disclaimer: Consume with moderation, healthy, doesn´t mean: eat all you can.
Lean proteins
Lean proteins like fish, poultry (chicken, turkey, quail, etc.), lean meats (beef, pork) and legumes support tissue repair (especially after surgery), immune cell production, and promote lymphatic health.
Anti-inflammatory spices
Reduce cellular inflammation and support circulation. Most used in kitchen are:
Turmeric (curcumin is the active compound, activate it with black pepper, ginger, cinnamon, cloves, cardamom, star anise, chili peppers (capsaicin), cayenne pepper, paprika, garlic, black pepper ( remember piperine enhances curcumin absorption), fennel seeds, mustard seeds, coriander seeds, cumin, etc.
High in water vegetables and fruits
Help detoxification and fluid balance due to their high water and low fructose and sodium content, like: cucumber, celery and watermelon.
2.Hydrate to flow well
Lymph fluid is primarily water, so maintaining adequate hydration is crucial to keep the lymphatic system moving and prevent fluid stagnation. Aim for 8–10 glasses of water daily, adjusting for activity level and climate.
3.Limit sodium and processed foods to avoid fluid retention
High sodium intake causes water retention, increasing swelling and lymphatic overburden. Avoid processed and fast foods because they tend to be high in salt and additives that exacerbate inflammation and fluid retention.
4.Probiotics and fiber for digestive and immune health
Probiotics (found in yogurt, kefir, fermented food, etc.) and prebiotics: Fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables aid digestion and promote a healthy gut microbiome. The gut microbiota reduce systemic inflammation and regulate mental and immune function while, indirectly, benefiting the lymphatic system’s function.
In short
Post-surgical lymphatic nutrition is a cornerstone of lymphoedema prevention and recovery after orthopaedic surgery. A diet focused on reducing inflammation, supporting immune function, maintaining hydration, and providing necessary nutrients optimises lymphatic healing and reduces swelling risk. Combined with MLD, physical therapy, compression (if needed), and medical follow-up, proper nutrition gives you the power to support your lymphatic and general wellbeing after orthopaedic or any type of surgery.
We hope this information is useful for you. If you need advice or have any questions about our treatments, please contact us. You can find us in Mill Hill Broadway and Islington. We are always happy to help. If you like this blog, please share!
References:
https://pereaclinic.com/nutrition-and-lymphedema-foods-that-support-a-healthy-lymphatic-system/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36252267/
https://www.pagepressjournals.org/index.php/vl/article/view/8220