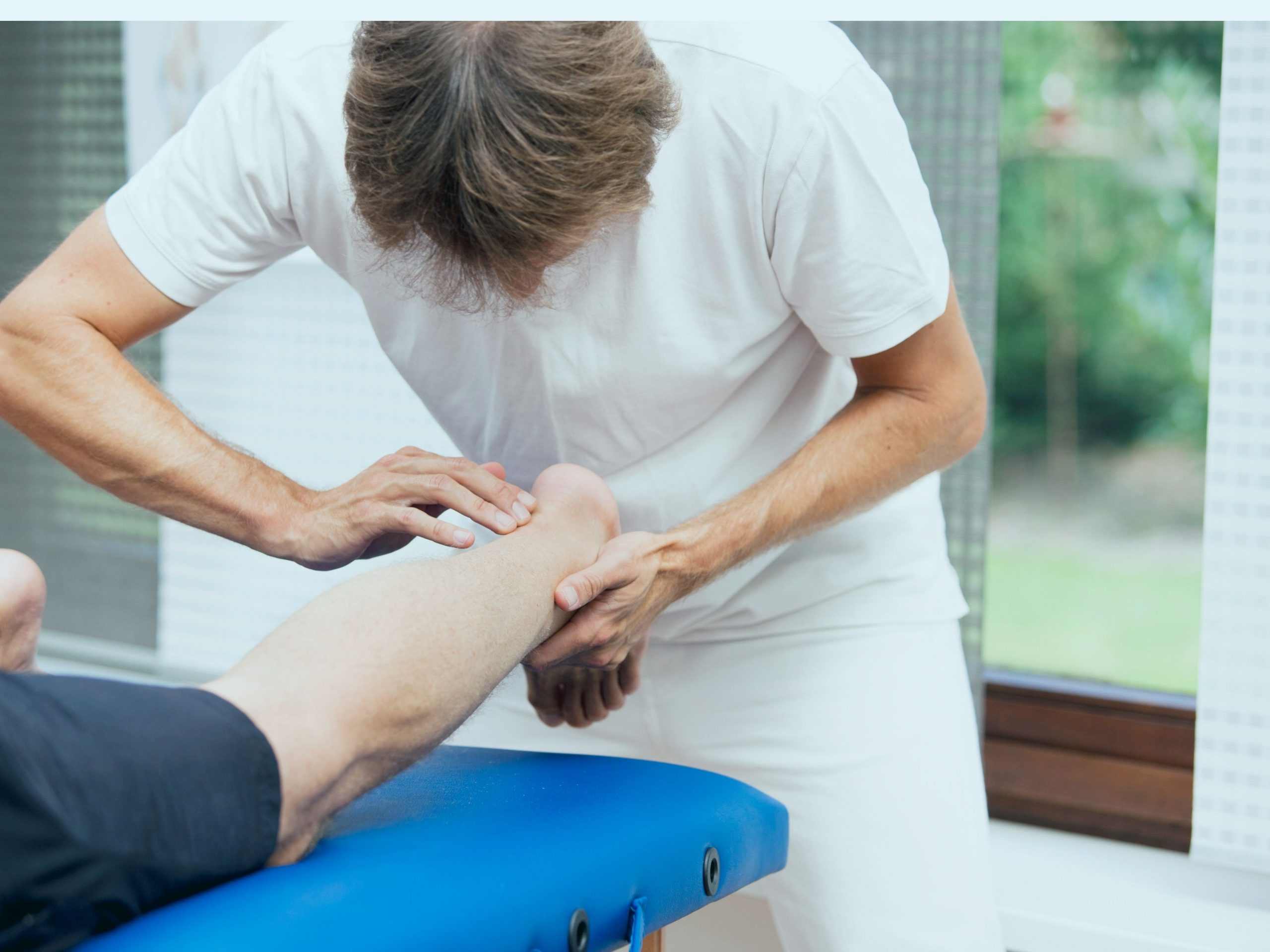
How to treat tendonitis
What is tendonitis?
Tendonitis is very often used interchangeably with tendinitis. Both terms have the same meaning. Tendonitis is an inflammation of a tendon which usually results in swelling, redness, and increase in temperature of the affected area. The affected tendon is usually painful during physical activity, very sensitive to touch and might feel stiff and achy in the morning. You might also experience reduced range of movement of a joint closest to the affected tendon.
What causes tendonitis?
There are few aspects which can contribute to the development of a tendonitis. It can be caused acutely if you make a sudden sharp movement or it may be a result of an overuse injury during repetitive physical activities such as throwing, running, cycling and swimming. Tendonitis can also be a by product of poor biomechanics and poorly fitted training gear.
How tendinopathy differs from tendonitis/tendinitis?
Tendinopathy is an umbrella term to describe everything that affects tendons, including tendonitis, tendon strains, degeneration of a tendon, inflammation of tendon sheath and more.
What treatment options are available for tendonitis?
The range of treatment varies from changing the sports gear to having some invasive alternatives such as corticosteroid injections. This usually is determined by the degree of tendonitis including factors such as symptom duration, intensity of pain, activity level and desirable outcome. Some of the most common approaches to treat tendonitis are below:
Non-invasive treatments
Exercise Therapy – eccentric loading appears to be one of the most effective exercises when it comes to treating tendonitis. Eccentric loading means muscle being contracted while lengthening, in other words, stretching under tension. This type of exercise can also be combined with static stretches, strengthening and foam rolling.
Massage – massage, particularly the friction, is another alternative therapy technique to treat tendonitis. Friction is a strong, deep pressure technique applied on the painful spot and held for several minutes with very minimal movement. It is usually quite uncomfortable and is used to break down adhesions and tender areas in the muscles and tendons.
Appliance treatments
Ultrasound – ultrasound therapy is one of the electrotherapy modalities which sends continuous sound waves into the affected area to enhance the healing of the tissue. It is most effective when works in conjunction with other types of treatments such as exercise therapy and massage.
Shock wave therapy – shock wave therapy is another electrotherapy modality to treat tendonitis. It is much stronger than the ultrasound, although, just like ultrasound, it sends sound vibrations into the tissue to promote the circulation and enhance proliferation, which refers to rapid reproduction of cells. There is a reasonable amount of evidence suggesting that shockwave therapy is an effective modality on its own.
Invasive treatment
Corticosteroid injection – is an invasive method when it comes to treating tendonitis. During the treatment, the therapist injects the affected area with the corticosteroid which helps to manage inflammation and pain. However, experts recommend to employ exercise therapy as soon as you possible after the injection to help strengthen the tendon as number of injections are limited and having too many may weaken the area.
How long is the recovery process?
Unfortunately, we are unable to give you a straight forward answer because there are many variables. It depends on the duration of the tendonitis, severity of symptoms, frequency of irritation, treatment undertaken, activity levels and more. Generally, it may take anywhere between few weeks to several months.
Can I exercise if I have tendonitis?
In short, yes you can. However, physical activity that you want to undertake must be adjusted so that the tendonitis is not being irritated, otherwise it can make your symptoms worst and prolong the healing period.
Is tendonitis permanent?
You have a very high chance to treat your tendonitis successfully if you start looking after it as soon as you can. If you will allow it to linger, it might become chronic which can alter your biomechanics placing excessive strain on other structures such as muscles and joints.
We hope this information is useful for you. If you have any questions about our treatments, please contact us. You can find us in Mill Hill Broadway and Islington. If you like this blog, please share!
We are always happy to help.
References:
http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.621.506&rep=rep1&type=pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3070010/pdf/12178_2010_Article_9067.pdf